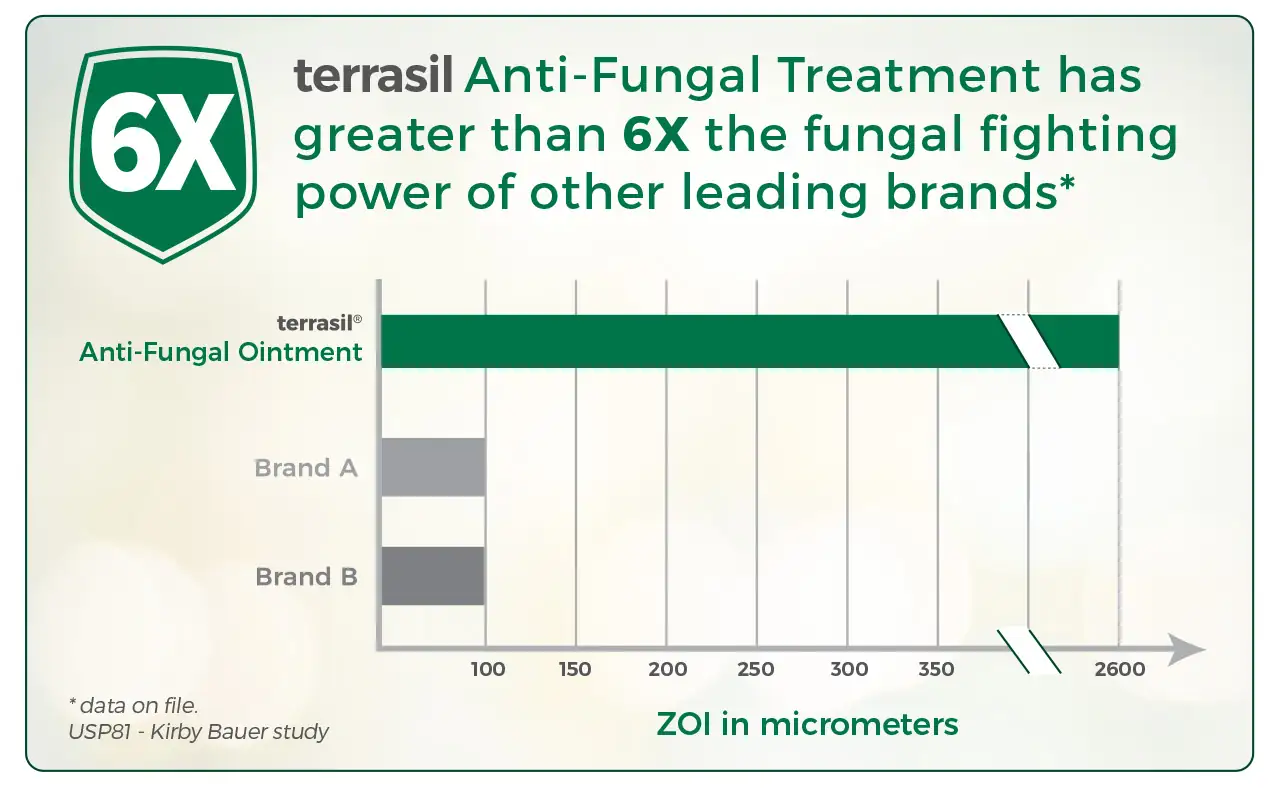
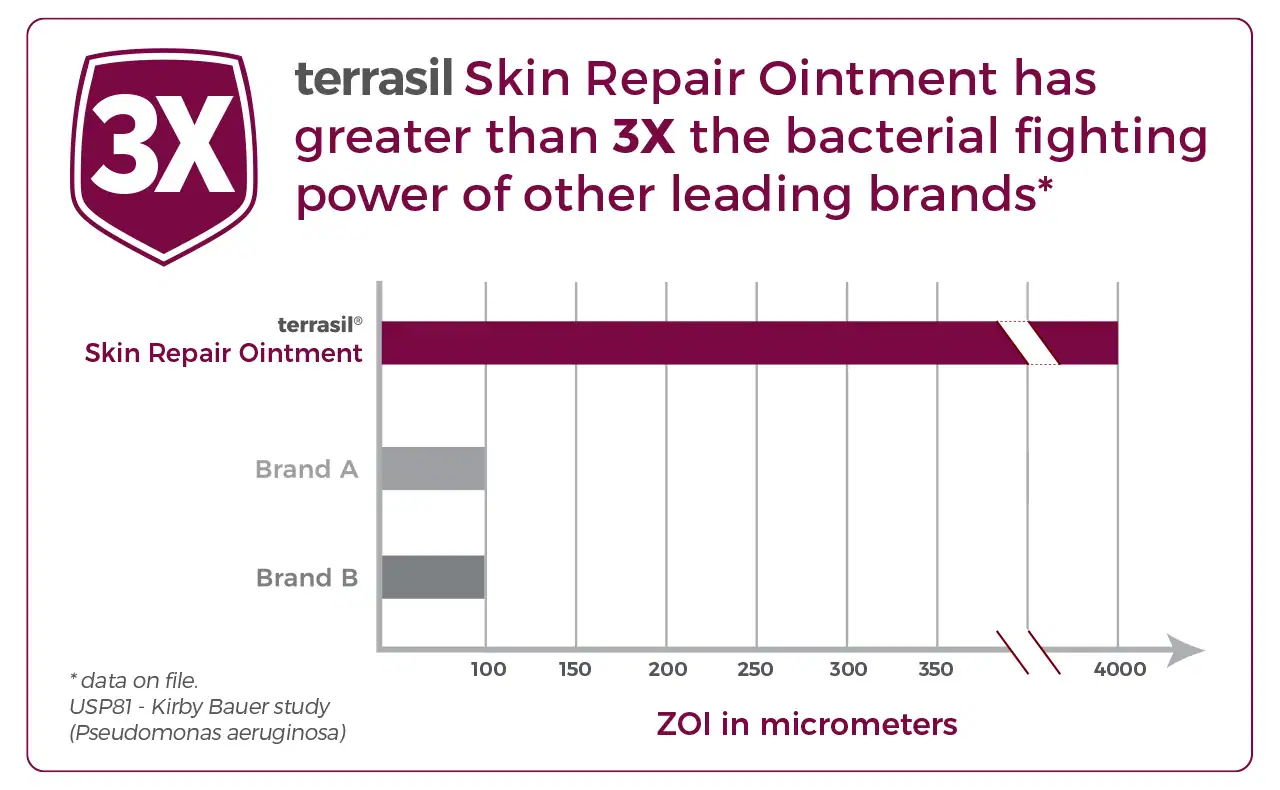
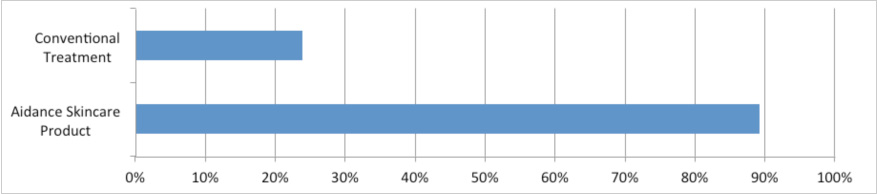
Background: Tea tree oil is the essential oil steam-distilled from Melaleuca alternifolia, an Australian native plant. In recent years it has become increasingly popular as an antimicrobial for the treatment of conditions such as tinea pedis and acne. Objectives:: To investigate the anti-inflammatory properties of tea tree oil on histamine-induced weal and flare. Methods: Twenty-seven volunteers were injected intradermally in each forearm (study and control assigned on an alternating basis) with histamine diphosphate (5 microg in 50 microL). Flare and weal diameters and double skin thickness were measured every 10 min for 1 h to calculate flare area and weal volume. At 20 min, 25 microL of 100% tea tree oil was applied topically to the study forearm of 21 volunteers. For six volunteers, 25 microL paraffin oil was applied instead of tea tree oil. Results: Application of liquid paraffin had no significant effect on histamine-induced weal and flare. There was also no difference in mean flare area between control arms and those on which tea tree oil was applied. However, mean weal volume significantly decreased after tea tree oil application (10 min after tea tree oil application, P = 0.0004, Mann-Whitney U-test). Conclusions: This is the first study to show experimentally that tea tree oil can reduce histamine-induced skin inflammation.
Satchell AC, Saurajen A, Bell C, Barnetson RS. Treatment of interdigital tinea pedis with 25% and 50% tea tree oil solution: a randomized, placebo-controlled, blinded study. Australas J Dermatol. 2002 Aug;43(3):175-8. PubMed PMID: 12121393. Tea tree oil has been shown to have activity against dermatophytes in vitro. We have conducted a randomized, controlled, double-blinded study to determine the efficacy and safety of 25% and 50% tea tree oil in the treatment of interdigital tinea pedis. One hundred and fifty-eight patients with tinea pedis clinically and microscopy suggestive of a dermatophyte infection were randomized to receive either placebo, 25% or 50% tea tree oil solution. Patients applied the solution twice daily to affected areas for 4 weeks and were reviewed after 2 and 4 weeks of treatment. There was a marked clinical response seen in 68% of the 50% tea tree oil group and 72% of the 25% tea tree oil group, compared to 39% in the placebo group. Mycological cure was assessed by culture of skin scrapings taken at baseline and after 4 weeks of treatment. The mycological cure rate was 64% in the 50% tea tree oil group, compared to 31% in the placebo group. Four (3.8%) patients applying tea tree oil developed moderate to severe dermatitis that improved quickly on stopping the study medication.
Buck DS, Nidorf DM, Addino JG. Comparison of two topical preparations for the treatment of onychomycosis: Melaleuca alternifolia (tea tree) oil and clotrimazole. J Fam Pract. 1994 Jun;38(6):601-5. PubMed PMID: 8195735. Background: The prevalence of onychomycosis, the most frequent cause of nail disease, ranges from 2% to 13%. Standard treatments include debridement, topical medications, and systemic therapies. This study assesses the efficacy and tolerability of topical application of 1% clotrimazole solution compared with that of 100% Melaleuca alternifolia (tea tree) oil for the treatment of toenail onychomycosis. Methods: A double-blind, multicenter, randomized controlled trial was performed at two primary care health and residency training centers and one private podiatrist's office. The participants included 117 patients with distal subungual onychomycosis proven by culture. Patients received twice-daily application of either 1% clotrimazole (CL) solution or 100% tea tree (TT) oil for 6 months. Debridement and clinical assessment were performed at 0, 1, 3, and 6 months. Cultures were obtained at 0 and 6 months. Each patient's subjective assessment was also obtained 3 months after the conclusion of therapy. Results: The baseline characteristics of the treatment groups did not differ significantly. After 6 months of therapy, the two treatment groups were comparable based on culture cure (CL = 11%, TT = 18%) and clinical assessment documenting partial or full resolution (CL = 61%, TT = 60%). Three months later, about one half of each group reported continued improvement or resolution (CL = 55%; TT = 56%). Conclusions: All current therapies have high recurrence rates. Oral therapy has the added disadvantages of high cost and potentially serious adverse effects. Topical therapy, including the two preparations presented in this paper, provide improvement in nail appearance and symptomatology. The use of a topical preparation in conjunction with debridement is an appropriate initial treatment strategy.
Tong MM, Altman PM, Barnetson RS. Tea tree oil in the treatment of tinea pedis. Australas J Dermatol. 1992;33(3):145-9. PubMed PMID: 1303075. Abstract Tea tree oil (an essential oil derived primarily from the Australian native Melaleuca alternifolia) has been used as a topical antiseptic agent since the early part of this century for a wide variety of skin infections; however, to date, the evidence for its efficacy in fungal infections is still largely anecdotal. One hundred and four patients completed a randomized, double-blind trial to evaluate the efficacy of 10% w/w tea tree oil cream compared with 1% tolnaftate and placebo creams in the treatment of tinea pedis. Significantly more tolnaftate-treated patients (85%) than tea tree oil (30%) and placebo-treated patients (21%) showed conversion to negative culture at the end of therapy (p < 0.001); there was no statistically significant difference between tea tree oil and placebo groups. All three groups demonstrated improvement in clinical condition based on the four clinical parameters of scaling, inflammation, itching and burning. The tea tree oil group (24/37) and the tolnaftate group (19/33) showed significant improvement in clinical condition when compared to the placebo group (14/34; p = 0.022 and p = 0.018 respectively). Tea tree oil cream (10% w/w) appears to reduce the symptomatology of tinea pedis as effectively as tolnaftate 1% but is no more effective than placebo in achieving a mycological cure. This may be the basis for the popular use of tea tree oil in the treatment of tinea pedis.
Bassett IB, Pannowitz DL, Barnetson RS. A comparative study of tea-tree oil versus benzoylperoxide in the treatment of acne. Med J Aust. 1990 Oct 15;153(8):455-8. PubMed PMID: 2145499. Tea-tree oil (an essential oil of the Australian native tree Melaleuca alternifolia) has long been regarded as a useful topical antiseptic agent in Australia and has been shown to have a variety of antimicrobial activities; however, only anecdotal evidence exists for its efficacy in the treatment of various skin conditions. We have performed a single-blind, randomised clinical trial on 124 patients to evaluate the efficacy and skin tolerance of 5% tea-tree oil gel in the treatment of mild to moderate acne when compared with 5% benzoyl peroxide lotion. The results of this study showed that both 5% tea-tree oil and 5% benzoyl peroxide had a significant effect in ameliorating the patients' acne by reducing the number of inflamed and non-inflamed lesions (open and closed comedones), although the onset of action in the case of tea-tree oil was slower. Encouragingly, fewer side effects were experienced by patients treated with tea-tree oil.
Tea tree oil as a novel antipsoriasis weapon. Pazyar N, Yaghoobi R. Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 2012;25(3):162-3. doi: 10.1159/000337936. Epub 2012 Apr 3. Psoriasis is a clinical skin disease that is characterized by erythematous scaling plaques and involves the extensor site of the extremities, the scalp and other surfaces of the skin. Tea tree oil (TTO) is considered an essential oil, obtained by steam distillation of the leaves and terminal branchlets of Melaleuca alternifolia. Notably,terpinen-4-ol, the major TTO constituent, has been found to have potent anti-inflammatory properties. It is suggested that terpinen-4-ol may be a novel potential agent against psoriasis. This article draws attention to the antipsoriatic effect of TTO and provides a theoretical molecular approach.
Tea tree oil attenuates experimental contact dermatitis. Wallengren J. Arch Dermatol Res. 2011 Jul;303(5):333-8. doi: 10.1007/s00403-010-1083-y. Epub 2010 Sep 24. Herbs and minerals have been used in clinical dermatology for hundreds of years and herbal ingredients are becoming increasingly popular with the public in treatment of various dermatological conditions characterised by inflammation and pruritus. The aim of this study was to compare the efficacy of traditional topical therapeutic agents with a moderate potency topical glucocorticoid on experimental contact dermatitis and contact urticaria. The effects of ichthammol 10% pet, zinc oxide 20% pet, camphor 20% pet, levomenthol 10% pet, tea tree oil 20 or 50% and clobetason butyrate 0.05% ointment were studied in the following experimental models: elicitation of allergic contact dermatitis to nickel, irritant contact dermatitis to benzalkonium chloride, and in immediate reactions to histamine and benzoic acid (non-immunological contact utricaria) respectively. Delayed reactions were evaluated using a clinical scoring system and immediate reactions were estimated by planimetry. Histamine-induced pruritus was evaluated using VAS. Tea tree oil reduced allergic contact dermatitis by 40.5% (p = 0.003), zinc oxide by 17.4% (p = 0.04) and clobetason butyrate by 23.5% (p = 0.01). Zinc oxide reduced histamine induced flare by 18.5% (p = 0.01), ichthammol by 19.2% (p = 0.02) and clobetason butyrate by 44.1% (p = 0.02). Irritant contact dermatitis and non-immunological contact urticaria were not influenced by the pre-treatments. Pruritus induced by histamine also remained unchanged. In conclusion, tea tree oil seems to be a more effective anti-eczematic agent than zinc oxide and clobetasone butyrate, while clobetasone butyrate is superior to both ichthammol and zinc oxide in topical treatment of urticarial reactions.
Nenoff, P., Haustein, U. F., and Brandt, W. Antifungal activity of the essential oil of Melaleuca alternifolia (tea tree oil) against pathogenic fungi in vitro. Skin Pharmacol 1996;9(6):388-394. The in vitro antifungal activity of tea oil, the essential oil of Melaleuca alternifolia, has been evaluated against 26 strains of various dermatophyte species, 54 yeasts, among them 32 strains of Candida albicans and other Candida sp. as well as 22 different Malassezia furfur strains. Minimum inhibitory concentrations (MIC) of tea tree oil were measured by agar dilution technique. Tea tree oil was found to be able to inhibit growth of all clinical fungal isolates. For the investigated dermatophytes MIC values from 1,112.5 to 4,450.0 micrograms/ml with a geometric mean of 1,431.5 micrograms/ml were demonstrated. Both C. albicans strains and the other strains belonging to the genus Candida and Trichosporon appeared to be slightly less susceptible to tea tree oil in vitro. However, their MIC values, which varied from 2,225.0 to 4,450.0 micrograms/ml (geometric mean 4,080 micrograms/ml), indicated moderate susceptibility to the essential oil of M. alternifolia. The lipophilic yeast M. furfur seemed to be most susceptible to tea tree oil. MIC values between 556.2 and 4,450.0 micrograms/ml (geometric mean 1,261.5 micrograms/ml) were found against the tested M. furfur strains. However, when calculated as percentage tea tree oil of the agar, the above-mentioned concentrations correspond to 0.5-0.44% tea tree oil content. These values are far below the usual relatively high therapeutic concentrations of the agent; approximately 5-10% solution or even the concentrated essential oil are used for external treatment. In comparison with tea tree oil, in vitro susceptibility against miconazole, an established topical antifungal, was tested. As expected, very low MIC values for miconazole were found for dermatophytes (geometric mean 0.2 microgram/ml), yeasts (geometric mean 1.0 microgram/ml), and M. furfur (geometric mean 2.34 micrograms/ml). It is suggested that the in vivo effect of tea tree oil ointment in the therapy of fungal infections of the skin and mucous membranes as well as in the treatment of dandruff, a mild form of seborrheic dermatitis, may be at least partly due to an antifungal activity of tea tree oil.
Successful topical treatment of hand warts in a paediatric patient with tea tree oil (Melaleuca alternifolia). Millar BC, Moore JE. Complement Ther Clin Pract. 2008 Nov;14(4):225-7. Epub 2008 Jul 11. Tea tree oil (TTO) (Melaleuca alternifolia) has been used recently as an effective topical application for the treatment of skin infections due to a variety of aetiological microbial agents, including mainly bacterial infections. We detail the first report in the peer-reviewed literature of the successful treatment with TTO of a paediatric patient with warts on her right middle finger. TTO was applied topically once daily to the lesions for 12 days, with a successful outcome, including complete re-epithelization of the infected areas. The case highlights the potential use of TTO in the treatment of common warts due to human papilloma virus.